SAP
SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products) is a comprehensive enterprise resource planning (ERP) software that streamlines supply chain management, supporting seamless operations. SAP offers various modules that manage different aspects of the supply chain, including procurement, production planning, and logistics execution. This comprehensive approach optimizes supply chains, balancing supply and demand, minimizing costs, and ensuring timely deliveries. SAP’s integration with existing systems and real-time tracking enhances visibility throughout the supply chain, supporting seamless operations and business success.
SAP has evolved significantly over time, expanding to support various aspects of supply chain management. Initially focused on financial accounting, SAP has grown to encompass modules for procurement, production, and logistics, supporting end-to-end supply chain operations. This evolution reflects the increasing complexity of supply chains and the demand for integrated solutions. SAP’s growth has led to the development of new modules and features, including real-time tracking, data analytics, and technological integration, supporting efficient supply chain operations.
This article aims to explore how SAP supports operational efficiency, technological integration, and business success in supply chain management. It will cover the various modules of SAP, including procurement, inventory management, production planning, and logistics execution. The article will also delve into how SAP enhances operational efficiency, integrates with existing systems, and supports collaboration. Additionally, it will explore the challenges and solutions of SAP implementation, future trends, and how SAP contributes to seamless operations and sustained success.
SAP Modules: Comprehensive Support for Supply Chain
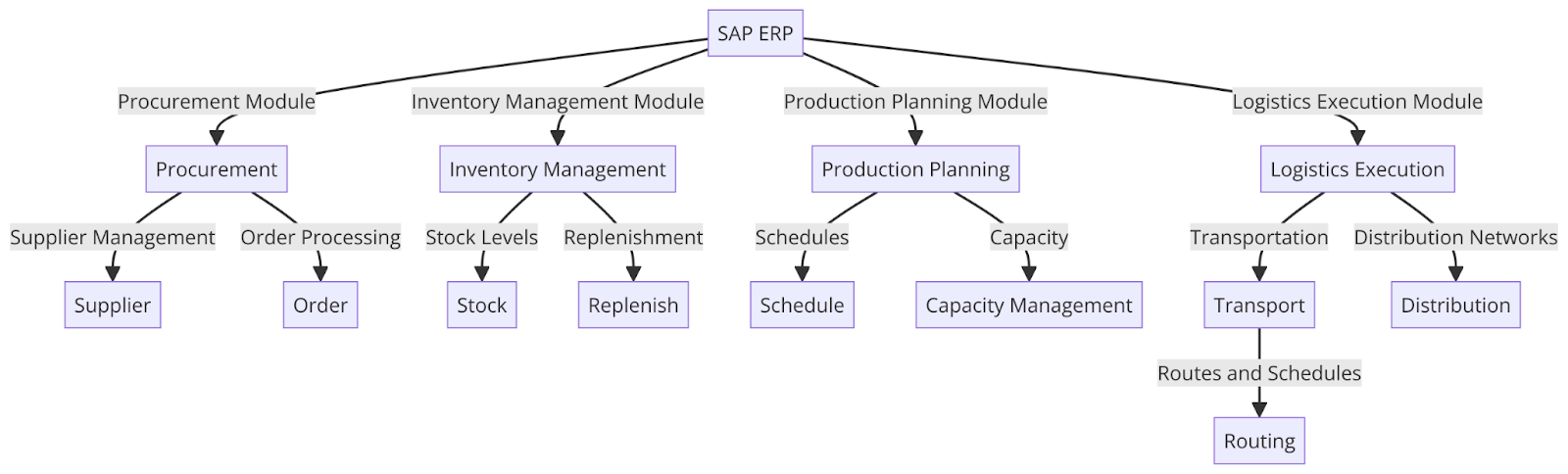
This diagram depicts the SAP ERP system’s key modules—Procurement, Inventory Management, Production Planning, and Logistics Execution—and their specific functions within the supply chain, highlighting how they interconnect to streamline operations.”
Procurement and Inventory Management
SAP manages procurement processes and inventory levels, balancing supply and demand throughout the supply chain. The procurement module streamlines supplier management, contract negotiations, and order processing, ensuring consistent resources. Inventory management tracks stock levels, manages replenishment, and balances supply and demand, minimizing overstocking and reducing storage costs. This comprehensive approach supports seamless supply chains, optimizing procurement and inventory management.
Production Planning
SAP coordinates production schedules, manages capacity, and oversees manufacturing processes, ensuring efficient production. The production planning module balances production schedules with demand levels, reducing bottlenecks and supporting seamless operations. This involves managing production capacities, tracking manufacturing processes, and ensuring timely deliveries. SAP’s integration with inventory management and logistics execution modules enhances coordination, supporting end-to-end supply chain operations.
Logistics Execution
SAP oversees transportation, distribution networks, and order fulfillment, ensuring seamless supply chain operations. The logistics execution module manages transportation routes, carrier networks, and delivery schedules, balancing speed with cost-effectiveness. This module also coordinates distribution networks, including warehousing, inventory management, and order fulfillment, supporting efficient distribution. SAP’s real-time tracking technology enhances visibility, allowing for proactive management and minimizing disruptions. This comprehensive approach supports seamless logistics operations, ensuring goods reach customers efficiently.
Operational Efficiency: SAP’s Impact on Supply Chain Management
Process Automation
SAP automates various supply chain processes, reducing human error and increasing productivity. This automation streamlines repetitive tasks, including order processing, inventory management, and procurement. The system integrates with other modules, ensuring seamless workflows and minimizing manual intervention. Automation enhances overall efficiency by reducing processing times, improving accuracy, and freeing up resources for strategic decision-making. This comprehensive approach supports seamless supply chain operations, balancing productivity with consistency.
Data Analytics
SAP leverages data analytics to forecast demand, optimize inventory, and support decision-making. The system collects and analyzes historical data, market trends, and sales patterns, providing insights into consumer behavior. These insights enable supply chain managers to forecast demand accurately, adjust inventory levels, and balance supply and demand. Data analytics also supports strategic decision-making, identifying areas for improvement, optimizing procurement processes, and enhancing performance. This balanced approach supports efficient supply chain management, minimizing costs and supporting business success.
Real-Time Tracking
SAP provides real-time tracking throughout the supply chain, enhancing visibility and minimizing disruptions. This tracking technology monitors goods at every stage, from procurement to distribution, allowing for proactive management. Real-time tracking provides accurate delivery estimates, identifies potential delays, and supports seamless distribution networks. It also enables supply chain managers to monitor shipments, manage transportation routes, and address potential disruptions, ensuring timely deliveries. This comprehensive tracking supports efficient logistics operations, reducing delays and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Integration and Collaboration: Enhancing Supply Chain Networks
System Integration
SAP integrates with existing systems, streamlining supply chain management and supporting efficient operations. This integration includes connecting various modules, including procurement, production planning, and logistics execution, ensuring seamless workflows. System integration also incorporates external systems, including CRM software, financial systems, and inventory management tools, balancing operational efficiency with data management. By streamlining these systems, SAP supports seamless supply chain operations, enhancing coordination and minimizing disruptions.
Supplier Collaboration
SAP facilitates collaboration with suppliers, managing relationships, contracts, and procurement processes. This collaboration includes overseeing supplier negotiations, establishing service level agreements (SLAs), and tracking supplier performance. SAP’s procurement module manages orders, delivery schedules, and contract terms, ensuring consistent procurement. By facilitating collaboration with suppliers, SAP supports balanced supply chains, minimizing costs, and reducing disruptions. This comprehensive approach enhances supply chain operations, supporting seamless procurement processes.
Cross-Departmental Coordination
SAP supports coordination between departments, balancing procurement, production, and distribution. This coordination ensures efficient workflows, reducing bottlenecks and supporting seamless supply chain operations. SAP integrates with various departments, including marketing, finance, and production, ensuring cohesive operations. Cross-departmental coordination also supports strategic decision-making, balancing resources, reducing costs, and enhancing performance. This balanced approach supports seamless supply chain operations, enhancing coordination and business success.
Challenges and Solutions: Navigating SAP Implementation
Change Management
Change management is a key aspect of implementing SAP, balancing training, communication, and adaptation. Introducing SAP requires comprehensive training programs, covering various modules, workflows, and processes. Communication is essential throughout the implementation, ensuring that all departments understand the system’s capabilities and integration. Adapting to SAP involves managing resistance to change, balancing existing processes with new workflows, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. This balanced approach to change management supports seamless SAP implementation, enhancing supply chain operations.
Data Security
SAP ensures data security, protecting sensitive information and supporting compliance throughout supply chain management. This involves implementing encryption measures, access controls, and regular audits to safeguard data. SAP integrates with existing security systems, balancing operational efficiency with data protection. Data security is crucial for maintaining customer trust, supporting regulatory compliance, and minimizing risks. By ensuring comprehensive security measures, SAP supports seamless supply chain operations, protecting sensitive information and maintaining business success.
System Updates
Companies navigate system updates, balancing technological advancements with seamless operations. This involves regularly evaluating SAP updates, assessing their impact on existing workflows, and implementing them to enhance efficiency. System updates integrate new features, including real-time tracking, data analytics, and process automation, supporting seamless supply chain management. Companies manage updates to minimize disruptions, balancing new technologies with existing processes. This comprehensive approach ensures that system updates enhance SAP operations, supporting efficient workflows.
Future Trends: SAP and Supply Chain Management
Digital Transformation
The continued integration of technology in SAP supports digital transformation and enhances supply chain efficiency. Automation streamlines various processes, from order processing to inventory management, reducing manual intervention. Data analytics leverages historical data and market trends, supporting demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and strategic decision-making. Real-time tracking provides visibility throughout the supply chain, allowing proactive management of potential disruptions. This digital transformation balances technological advancements with effective management, supporting seamless supply chain operations.
Sustainability Practices
SAP supports sustainable supply chain practices, reducing carbon footprints and promoting eco-friendly solutions. This includes optimizing transportation routes to minimize emissions, utilizing electric vehicles, and adopting alternative fuels. SAP also integrates sustainability measures into warehousing, including energy-efficient lighting, recycling programs, and green building certifications. These sustainable practices support balanced supply chains, benefiting the environment and appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. By incorporating sustainable practices, SAP enhances company reputations, supporting long-term success.
Global Expansion
SAP supports global supply chains, navigating international markets, trade regulations, and cross-border distribution. This involves balancing procurement from international suppliers, managing global distribution networks, and navigating customs processes. SAP’s integration with global supply chains supports seamless operations, balancing international trade regulations with efficient workflows. By supporting global expansion, SAP enhances supply chain operations, allowing companies to reach new markets and support sustained growth.
Conclusion: SAP’s Role in Supply Chain Success
SAP streamlines supply chain management by offering various modules that support operational efficiency, integration, and collaboration. These modules manage procurement, inventory, production planning, and logistics execution, supporting end-to-end supply chain operations. SAP’s integration with existing systems, automation, and data analytics enhances operational efficiency, balancing workflows with effective management. By navigating industry challenges, incorporating sustainability practices, and supporting global expansion, SAP contributes to seamless operations, balancing business success and global commerce.