In today’s fast-paced business environment, supply chain management (SCM) stands as a cornerstone of operational efficiency and competitive advantage. The essence of SCM lies in orchestrating the flow of goods, information, and finances as they move from supplier to manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer and finally to the consumer. This intricate dance is not just about logistics; it’s about strategic foresight, pinpoint execution, and continuous improvement. Understanding the core elements of SCM is crucial for entrepreneurs aiming to carve out a niche in the marketplace, drive growth, and champion innovation and sustainability within their operations.
The Core Elements of Supply Chain Management
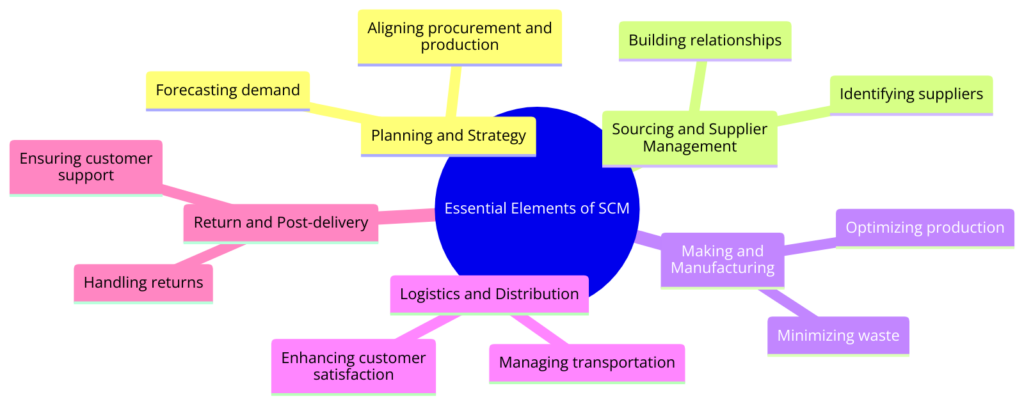
1. Planning and Strategy Development
Planning and strategy development form the backbone of effective SCM. It’s about forecasting demand accurately, coordinating procurement in sync with production schedules, and aligning these processes with logistics operations. The goal here is precision — delivering the right product, at the right time and place, and at the optimal cost. This stage sets the strategic direction and objectives of the entire supply chain, ensuring that every other element operates cohesively towards the business’s goals.
2. Sourcing and Supplier Management
The strength of a supply chain is significantly influenced by its suppliers. Sourcing and supplier management involve identifying and partnering with suppliers that can provide the necessary materials and services at competitive prices without compromising on quality. This element emphasizes the cultivation of robust, transparent relationships with suppliers to ensure a consistent, reliable flow of materials. Effective supplier management not only secures the supply chain but also fosters trust and collaborative efficiency across all stakeholders.
3. Making and Manufacturing
The making and manufacturing process is where raw materials are transformed into the final product. This stage is critical for optimizing production efficiency, minimizing waste, and maintaining high-quality standards. Employing principles of lean manufacturing and continuous improvement helps in streamlining operations, reducing costs, and enhancing product quality. It’s a dynamic process that requires constant evaluation and adaptation to meet changing market demands and technological advancements.
4. Logistics and Distribution
Logistics and distribution encompass the transportation, warehousing, and delivery of products to customers. This element ensures that products are available where and when customers need them, contributing significantly to customer satisfaction and loyalty. Efficient logistics and distribution networks are key to minimizing delivery times and costs, enhancing the overall customer experience.
5. Return and Post-delivery Management
An often overlooked but equally important aspect of SCM is return and post-delivery management. This involves handling returns, exchanges, and customer support following the sale. Effective management in this area can significantly impact customer satisfaction and trust. It’s about creating a seamless process for customers to return damaged or unsatisfactory products and ensuring prompt support and resolution of post-delivery issues.
Leveraging Technology for SCM Optimization
The digital revolution has ushered in a new era for supply chain management (SCM), characterized by unprecedented efficiency, transparency, and resilience. At the heart of this transformation are technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain, each playing a pivotal role in optimizing supply chain operations.
AI and machine learning algorithms are revolutionizing SCM by predicting market trends, optimizing inventory levels, and identifying the fastest, most cost-effective delivery routes. These intelligent systems can analyze vast datasets to forecast demand with remarkable accuracy, enabling businesses to adjust their supply chains dynamically in response to market shifts.
The IoT extends this intelligence across the physical components of the supply chain. Sensors and smart devices provide real-time data on the location, condition, and progress of goods throughout the supply chain, from the warehouse shelf to the customer’s doorstep. This constant stream of data enhances visibility, allowing companies to monitor their operations closely and respond swiftly to any disruptions or inefficiencies.
Blockchain technology offers an added layer of security and transparency, creating an immutable ledger of transactions that all parties in the supply chain can access. This not only reduces the risk of fraud and errors but also fosters trust among suppliers, shippers, and customers by providing a transparent, verifiable record of the movement and authenticity of goods.
Streamlining Success: The Core of Supply Chain Mastery
“Dive into the essential elements of SCM: From strategic planning to customer satisfaction, discover the pillars of supply chain success.”
In the intricate world of modern business, Supply Chain Management (SCM) emerges as a critical linchpin, driving efficiency and carving out competitive edges. At the heart of SCM lies a symphony of strategic elements, each playing a vital role in harmonizing the flow of goods, information, and finances across the global stage. These elements—Planning and Strategy, Sourcing and Supplier Management, Making and Manufacturing, Logistics and Distribution, and Return and Post-delivery Management—collectively weave the fabric of a successful supply chain.
Planning and Strategy Development serves as the compass, guiding businesses through the complexities of demand forecasting, procurement alignment, and logistical orchestration. It is where the strategic vision is set, aligning all operations towards the pinnacle of efficiency and market responsiveness.
Sourcing and Supplier Management underscores the importance of relationships in the supply chain. By meticulously selecting and nurturing partnerships with suppliers, businesses ensure a steady and reliable flow of quality materials, fostering trust and mutual growth.
Making and Manufacturing processes are the crucible where raw materials are transformed, embodying the principles of lean manufacturing and continuous improvement to enhance quality while minimizing waste.
Logistics and Distribution act as the arteries of the supply chain, ensuring the lifeblood of goods moves efficiently from creators to consumers, thus elevating customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Finally, Return and Post-delivery Management highlights the significance of customer service post-purchase, managing returns with ease and ensuring support that cements customer trust and satisfaction.
Incorporating these elements into your SCM strategy not only optimizes operations but also propels your business towards sustainable growth and innovation, proving that the essence of supply chain mastery lies in the seamless integration of its core elements.
Prioritizing Sustainability in Supply Chain Practices
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern SCM, driven by increasing consumer awareness, regulatory pressures, and a genuine corporate commitment to environmental stewardship. Sustainable supply chain practices focus on minimizing the environmental impact of logistics operations, from sourcing raw materials to delivering products to consumers.
One of the key areas of focus is the reduction of carbon emissions. Innovations such as electric vehicles (EVs) in logistics fleets and the optimization of transportation routes using AI can significantly lower the carbon footprint of supply chain operations. Additionally, companies are exploring alternative fuels and investing in carbon offset programs to further reduce their environmental impact.
Sustainable packaging solutions are also gaining traction, with businesses adopting biodegradable, recyclable, or reusable packaging materials to minimize waste. Moreover, companies are implementing circular economy principles into their supply chains, designing products with end-of-life recycling in mind and developing systems for refurbishing or recycling used products.
The Path to a Lucrative SCM Career
Embarking on a career in Supply Chain Management (SCM) opens up a realm of possibilities for aspiring professionals and entrepreneurs alike. The expansion of the industry, coupled with the increasing reliance on efficient supply chains by businesses across the globe, has spiked the demand for skilled SCM professionals. For those looking to navigate this promising career path, education serves as the foundation. A degree in SCM, business, or a related field equips individuals with the essential knowledge to kickstart their careers.
However, the learning doesn’t stop with graduation. The SCM field is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting global economic landscapes. Thus, certifications such as the Certified Supply Chain Professional (CSCP) or the Certified in Logistics, Transportation, and Distribution (CLTD) offer ways to demonstrate expertise and commitment to staying abreast of industry trends. Moreover, a commitment to continuous learning—whether through workshops, seminars, or further education—ensures professionals can adapt to and thrive in the dynamic SCM environment.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of SCM
In the vast and complex world of supply chain management, understanding and mastering the essential elements are critical for anyone aspiring to make a mark in this field. For entrepreneurs and professionals, the journey through SCM is not just about navigating operational challenges; it’s about seizing the opportunities that come with technological innovations and a growing focus on sustainability. By dedicating themselves to continuous education and embracing the shifts towards more eco-friendly and technologically advanced supply chain solutions, individuals can ensure they remain at the forefront of the industry. The future of SCM promises a landscape where operational excellence and sustainable growth go hand in hand, offering a rewarding path for those ready to explore its depths and contribute to its evolution.